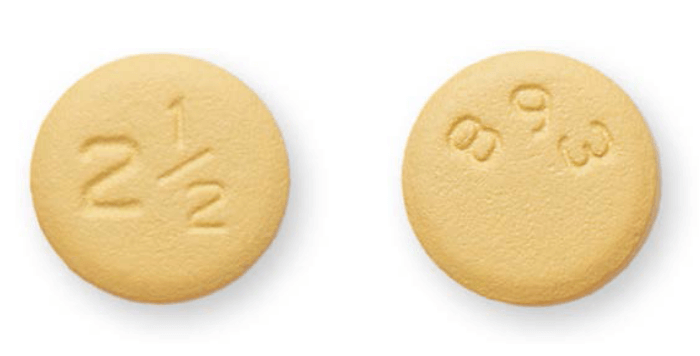
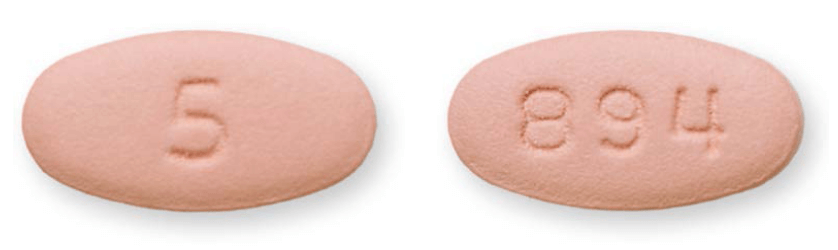
Eliquis Dosage, forms & strengths
Complete a free online enrollment application to find out if you’re eligible to pay only $49 per month for your Eliquis medication.
Get started todayEliquis, manufactured by Bristol-Myers Squibb and partner Pfizer is classed as a factor Xa inhibitor direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC). Eliquis basically stops the coagulation of your blood. It is FDA approved to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Eliquis is also used for the prevention and treatment of blood clots in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), in patients who have undergone hip replacement or knee replacement surgery.
Eliquis forms and strengths
Eliquis is available in two strengths, 2.5 mg tablets, and 5 mg tablets. Your recommended dosage will depend on the condition you are being treated for, your age, weight, and your renal function.
Eliquis dosage chart
| Indication | Initial dosage | Maintenance dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Non-valvular atrial fibrillation | 5 mg twice daily | 5 mg twice daily |
| DVT prophylaxis after hip or knee replacement surgery | 2.5 mg twice daily | 2.5 mg twice daily |
| DVT and PE prophylaxis due to recurrences | 2.5 mg twice daily | 2.5 mg twice daily |
| Acute DVT or PE treatment | 10 mg twice daily for 7 days | 5 mg twice daily after the first 5 days |
Eliquis dosage for adults
Eliquis dosage for stroke and thromboembolism prevention in atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a condition where blood does not flow in or out of the heart normally as it should. This can cause blood clots to form. Thromboembolism is when a blood clot in a blood vessel, breaks loose and is carried by the blood to block another blood vessel. When this happens in the brain it is called a stroke. Your risk of stroke with AF will depend on other factors such as your age, gender, and other conditions you may have.
The recommended dose of Eliquis in AF is 5 mg twice daily. Specifically for thromboembolism and stroke prevention in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation which is not associated with valvular heart abnormalities like prosthetic heart valves and moderate to severe mitral stenosis. Eliquis can be given at a lower dose prophylactically to reduce your risk of a thrombotic event. More clinical trials are needed on the use of Eliquis in valvular problems.
Eliquis dosage for prevention of DVT and PE
The risk of lower limb DVT is increased after knee and hip replacement surgery. Anticoagulants can be given before surgery however to prevent this. The recommended dose is 2.5 mg twice daily, starting 12 to 24 hours after surgery and continuing for 10 to 35 days. Length of treatment is based on patient factors. It should be noted that treatment is normally longer after hip replacement than knee replacement.
Eliquis dosage for treatment of acute DVT or PE
When a clot travels to the lung, it is known as a pulmonary embolism (PE). Eliquis is an option for the treatment of DVT and PE. The recommended standard dosage is 10 mg twice daily for seven days followed by 5 mg twice daily thereafter.
Eliquis dosage restrictions
A reduced dose of Eliquis may be needed based on renal function, age, and body weight.
- Renal impairment with AF – 2.5 mg twice daily if serum creatinine is greater than 1.5 mg/dL or if you are over 80 years of age or you weigh less than 60 kg or 132 pounds
- Severe renal impairment needing prophylaxis against DVT or PE – no dosing adjustments recommended
- Hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) – caution advised
- Hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) – not recommended
- Patients older than 80 with AF – 2.5 mg twice daily if serum creatinine is greater or equal to 1.5 mg/dL (or on dialysis) or you weigh up to 60 kg or 132 pounds
- Triple-positive antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) – do not take Eliquis if you have triple-positive APS as it may increase your risk for blood clots
Eliquis increases the risk of bleeding and can cause serious, potentially fatal, bleeding. Eliquis is not recommended if you have active pathological bleeding and severe hypersensitivity to Eliquis.
How to take Eliquis
- Warfarin should be discontinued and Eliquis started when the international normalized ratio (INR) is below 2.0
- Eliquis is taken orally. If you are unable to swallow the tablets whole, you may crush the tablets and mix them in water, apple juice, or applesauce. The crushed tablets may be mixed with 60 mL of water or D5W dose and given through a nasogastric tube
- If you forget to take your dose on time take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, wait until your next dose is due and take it then. Do not take extra medicine to make up for a missed dose
- Blood cell count, kidney, liver function, and natural clotting measurements (prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time) are normally taken. Routine monitoring of blood-thinning levels is not needed due to the predictable effects of Eliquis
- Please read the full prescribing information and the medication guide for the full patient safety information
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements before commencing treatment
Eliquis dosage FAQs
How long will it take for Eliquis to work?
Eliquis is fast-acting, you will see its effects within three to four hours.
How long will Eliquis work for?
Eliquis has a half-life of 8 to 12 hours. This means the concentration of Eliquis falls by 50% in 8 to 12 hours. After you stop taking Eliquis, 97% is eliminated from your body within two to three days.
How long can you take Eliquis?
Eliquis can be taken for the rest of your life for stroke and thromboembolism prevention in atrial fibrillation if you are at high-risk. You may need to take it for two to five weeks after knee or hip joint replacement and for three to six months after DVT or PE.
How do I stop taking Eliquis?
You may be at an increased risk of blood clots when stopping Eliquis. Discontinuation of Eliquis should be carried out under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Discontinuing Eliquis for spinal anesthesia or an epidural injection is particularly important due to the risk when a blood collection or hematoma forms within the spinal column.
What is the maximum dosage for Eliquis?
Your maximum apixaban dose depends on the condition you are being treated for, as well as any other medicines you may be taking.
Can you overdose on Eliquis?
Taking too high a dose can cause serious side effects of apixaban, such as major bleeding. In the event of an overdose, you should seek emergency medical care and call the Poison Control Helpline at 1-800-222-1222.
What drug interactions are there with Eliquis?
- CYP-3A4 enzyme and P-glycoprotein (P-GP) transporter inhibitors or inducers. Inhibitors such as ritonavir and ketoconazole can reduce the metabolism of Eliquis and consequently increase its blood-thinning action. Inducers can increase Eliquis’s metabolism and reduce its action
- Defibrotide and mifepristone use with Eliquis is contraindicated
- Blood thinners such as warfarin and heparin can cause adverse reactions when taken along with Eliquis
- Coadministration of antiplatelet agents such as aspirin may increase the risk of hemorrhage but may be necessary in some cases, such as coronary heart disease with atrial fibrillation
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen
- Antidepressants such as SSRIs or SNRIs
- Long-term concomitant treatment with edoxaban or dabigatran and other anticoagulants is not recommended
What happens when you mix Eliquis and alcohol?
Alcohol use could cause a higher risk of bleeding. Consuming alcohol with Eliquis is not recommended.
Is it safe to take Eliquis during pregnancy or when breastfeeding?
Alternative anticoagulants are advised for pregnant women or those breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed. You should discuss this with a healthcare professional before commencing treatment.
Related medications
Eliquis images
Eliquis tablet strengths